JUNA TECH Mass-Produces JP Series PEM Electrolysis MEAs
Targeting Industrial Applications for PEM Electrolysis MEAs
In large-scale industrial applications, outsourcing PEM MEAs has become an inevitable trend. Recognizing the gap in industrial-grade PEM MEAs, JUNA TECH has dedicated significant R&D efforts to overcoming technical challenges.
"From catalyst material development and proton exchange membrane selection to slurry formulation, coating, and transfer techniques, we have conducted extensive testing and validation in collaboration with customers. Our tests focused on MEA degradation, hydrogen crossover, and product consistency. Through repeated optimization cycles, we finalized a large-width slot-die coating + thermal transfer manufacturing process and have now completed the construction of a 100MW MEA production line."
— JUNA TECH R&D Team
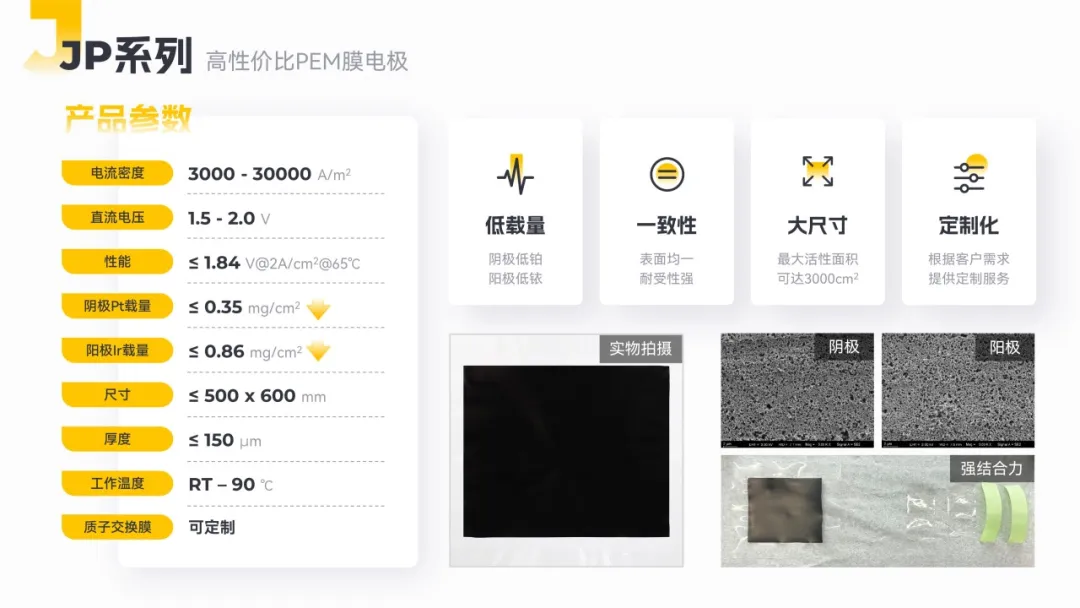
JP Series Key Parameters
From the outset, the JP Series was designed for industrial applications, ensuring plug-and-play functionality without requiring high-current activation—only simple in-line activation, eliminating the need for pre-treatment.
Leveraging its upcoming Electrolyzer Core Component Testing Platform, JUNA TECH has conducted extensive performance validation and compatibility testing on the JP Series MEAs.
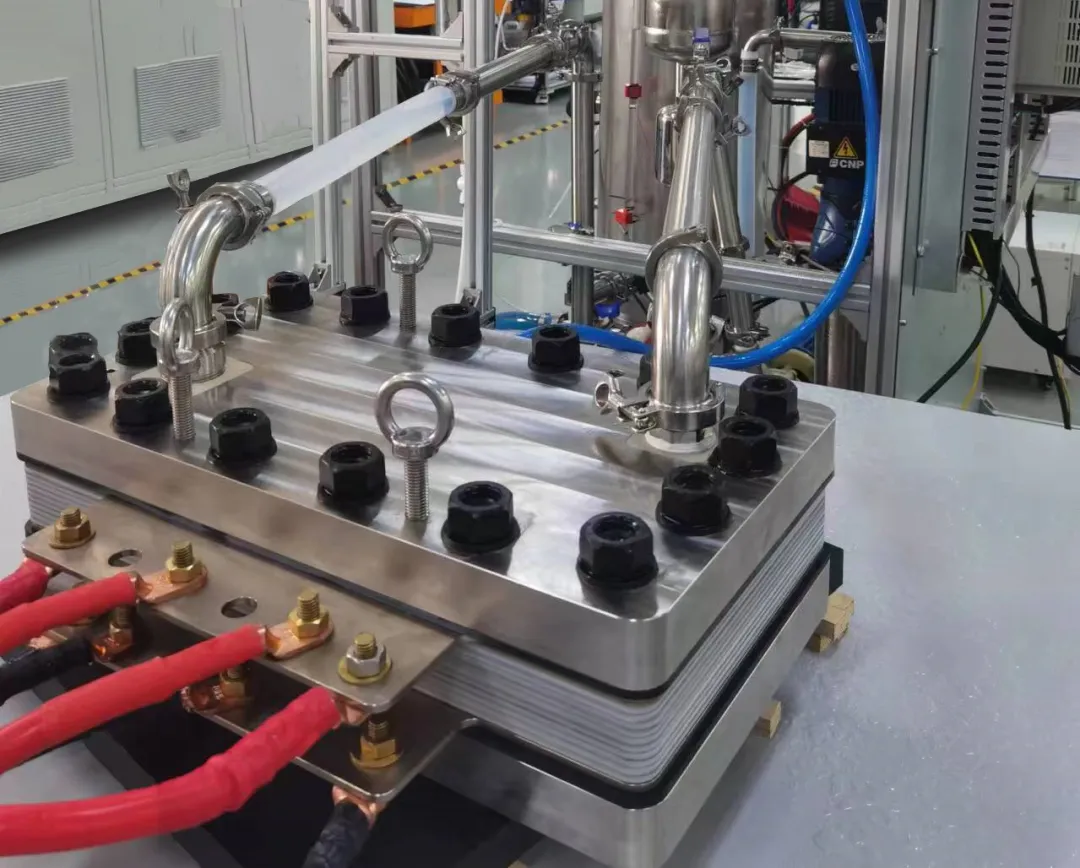

10 Nm³/h Electrolyzer Equipped with JP-30000 MEAs
Currently, JP-30000 MEAs (2A, N115, 60°C) have achieved over 1,900 hours of stable operation in laboratory tests, with a degradation rate controlled within 5μV/h and hydrogen content in oxygen as low as 0.34%.
Additionally, JUNA TECH has built multiple precision dual-temperature-controlled PEM MEA test stations (accuracy ±0.2°C) and a 10–20 Nm³/h electrolyzer testing platform for long-term stability tests and industrial electrolyzer performance validation.
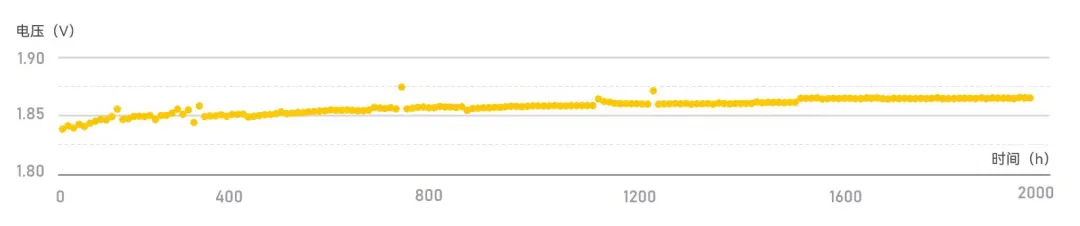
JP-30000 Stability Testing
"With extensive testing and experimentation, JUNA TECH aims to deliver industrial-grade PEM electrolysis MEAs that can be seamlessly integrated into commercial electrolyzers, contributing our expertise as a specialized green hydrogen materials provider to the advancement of the PEM electrolysis sector."
Ultra-Low Precious Metal Loading – Achieving a 20% Cost Reduction
Precious metal dependency is one of the biggest cost barriers in PEM electrolysis, particularly in the catalyst layers, where high platinum (Pt) and iridium (Ir) costs conflict with the need for large-scale cost reductions.
Currently, a 1MW PEM electrolyzer system (including balance-of-plant components) costs approximately ¥10 million, which is 3–5 times that of an equivalent alkaline electrolyzer.
MEAs account for 20–25% of total electrolyzer costs, with catalysts alone comprising ~30% of MEA costs. Typical cathode Pt loading ranges from 0.3–0.5 mg/cm², while anode iridium-based solutions often require 1–2 mg/cm² of Ir. However, iridium is one of the rarest precious metals, with an annual global production of only 5–10 tons (compared to ~200 tons of platinum). The low supply and high cost of iridium have made it a major bottleneck in PEM electrolysis scalability.
To address this, JUNA TECH has developed and optimized both cathode and anode catalysts:
- Cathode Catalyst: Pt alloy enhances active site synergy for higher efficiency.
- Anode Catalyst: Optimized slurry formulation and advanced dispersion processes have reduced Ir loading from >2 mg/cm² to 0.86 mg/cm², achieving a 20% cost reduction.
Additionally, JUNA TECH has leveraged its expertise in electrocatalysis and materials synthesis, making significant advancements in supported anode catalysts and structured electrode designs to enhance charge transfer efficiency and catalyst utilization.
"There is still significant room for further iterative improvements in slurry particle engineering and microstructure optimization. In large-scale production, process enhancements, waste reduction, and precious metal recycling and reuse will be critical for further cost reductions."
— JUNA TECH
Customized Solutions – Exploring the Optimal Domestic Alternative
PEM electrolyzers currently face structural design diversity, an immature core materials supply chain, and low domestic production rates—challenges that have hindered cost reductions and localization efforts.
To address these, JUNA TECH has developed a customizable JP Series PEM MEA solution.
"Our MEAs can support catalytically active areas up to 500×600mm, meeting diverse customer needs with tri-layer (CCM) and five-layer (MEA) configurations. We also provide industrial validation services to support large-scale deployment."
— JUNA TECH
By offering customized solutions, JUNA TECH is enabling the industry to explore the most optimal material combinations for domestic PEM electrolysis and providing crucial data to support localization-driven cost reductions.
According to GGII research, the domestic production rate of PEM electrolyzer core materials is currently below 50%, with imported proton exchange membranes (PEMs) dominating 90% of the industrial-scale market. Additionally, imported PEMs are priced at nearly twice the cost of domestic alternatives, making localization efforts essential for reducing PEM electrolyzer costs.
JUNA TECH has conducted a series of tests on domestically produced PEMs for PEM electrolysis. While its current mass-production products still utilize Chemours Nafion™ 115, some domestic PEMs have shown promising performance in early testing. JUNA TECH is now collaborating with domestic membrane manufacturers to refine performance and accelerate localization efforts.
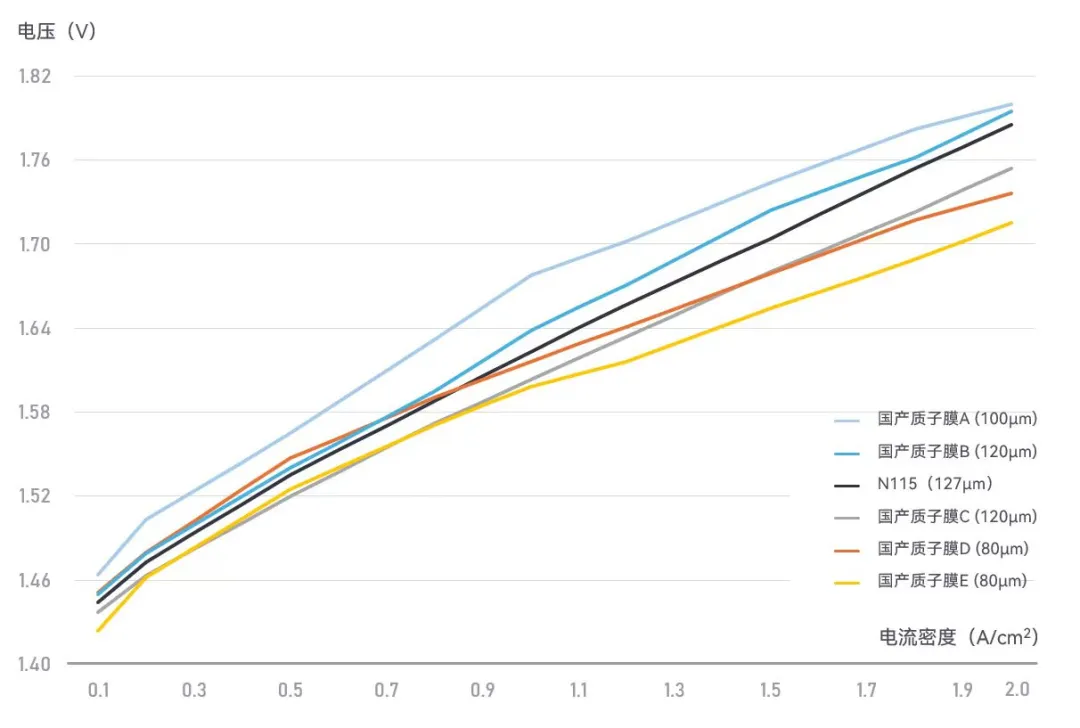
Performance Testing of JP-30000 Gen 2 with Different Proton Exchange Membranes @ 60°C
By combining cutting-edge catalyst technology with innovative manufacturing processes, JUNA TECH is breaking through industrial-scale MEA production bottlenecks. With a pragmatic yet innovation-driven approach, the company aims to further validate and optimize its products, supporting the scale-up of PEM electrolysis for green hydrogen production.
